The Magnoliaceae family, encompassing both tulip trees and magnolias, presents a fascinating study in botanical classification. Flower shape serves as a primary differentiator, showcasing distinct characteristics between the two. The Arnold Arboretum often features labeled specimens, aiding enthusiasts in identifying key differences. Understanding the query, are tulip trees magnolia, requires careful examination of leaf structure and overall growth habit. Botanists categorize these trees based on these precise morphological traits.

The natural world offers a tapestry of botanical wonders, and among the most admired are the majestic trees that grace our landscapes.
Two such trees, the Tulip Tree (Liriodendron tulipifera) and the Magnolia, often capture our attention with their impressive stature and captivating blooms.
However, their visual similarities can sometimes lead to confusion, prompting a common question: Are Tulip Trees Magnolias?
The short answer is no. While both trees share certain characteristics, they belong to different botanical families and possess distinct features that set them apart.
Addressing the Confusion
The confusion between Tulip Trees and Magnolias is understandable. Both are known for their elegant flowers and can be found in similar geographic regions.
Adding to the potential for misidentification is the fact that some Magnolias also boast a cup-shaped flower, superficially resembling the Tulip Tree’s namesake blooms.
Moreover, both are prized for their ornamental value, making them popular choices in parks, gardens, and residential landscapes.
Purpose of This Article
This article aims to dispel the ambiguity surrounding these two magnificent trees.
By providing clear and concise distinctions, we hope to empower readers with the knowledge necessary to accurately identify Tulip Trees and Magnolias.
We will explore their unique characteristics, focusing on key differences in their leaves, flowers, bark, and overall form.
Our goal is to offer a practical guide that will enable you to appreciate the individual beauty of each tree and confidently differentiate between them in any setting.
The Tulip Tree: A Unique Beauty
Having established the need for clarity in distinguishing between these arboreal beauties, let’s delve into the specific characteristics that define the Tulip Tree. This remarkable tree, with its distinctive features, stands as a testament to nature’s artistry.
Unveiling Liriodendron tulipifera
The Tulip Tree, scientifically known as Liriodendron tulipifera, is a true spectacle. Its botanical name itself hints at its unique attributes, Liriodendron meaning "lily tree" and tulipifera signifying "tulip-bearing." This nomenclature accurately reflects the tree’s most recognizable feature: its exquisite, tulip-like flowers. Beyond its blooms, however, the Tulip Tree boasts a collection of distinguishing characteristics that set it apart in the arboreal world.
Deciphering the Distinctive Foliage
The leaves of the Tulip Tree are undeniably unique.
They are easily identifiable by their distinctive shape, often described as saddle-shaped or lyre-shaped.
Unlike most leaves that taper to a point, the Tulip Tree’s leaves appear as though their tips have been cleanly cut off, resulting in a broad, flattened end. These leaves typically range from 3 to 8 inches in length and width, making them quite substantial and adding to the tree’s overall visual impact.
In spring and summer, the leaves display a vibrant, bright green hue, providing a lush canopy. As autumn approaches, they transform into a brilliant display of yellow and gold, contributing to the season’s picturesque landscapes.
The arrangement of leaves on the branches is alternate, meaning they are staggered along the stem rather than growing directly opposite each other.
The Allure of the Tulip-Like Flowers
Perhaps the most captivating feature of the Tulip Tree is its flowers. These blossoms, appearing in late spring to early summer, bear a striking resemblance to tulips, hence the tree’s common name.
The flowers are cup-shaped and typically measure 1.5 to 3 inches in diameter.
Their color is a delicate blend of yellow-green petals with an orange band near the base, creating a warm and inviting aesthetic.
The flowers stand upright on the branches, further enhancing their tulip-like appearance.
Although they are relatively high up in the tree and can be partially hidden by the leaves, their beauty is undeniable.
The flowers also emit a subtle, sweet fragrance that attracts pollinators like bees and hummingbirds.
A Study in Bark: Texture and Tone
The bark of the Tulip Tree undergoes significant changes as the tree matures.
In young trees, the bark is relatively smooth and greenish-gray in color.
As the tree ages, the bark develops a distinctive pattern of deep furrows and ridges, forming a reticulated, diamond-shaped pattern. This mature bark is typically gray to brown in color and provides an interesting textural element to the tree’s overall appearance. The deeply furrowed bark is not only visually appealing but also provides shelter for various insects and small organisms, contributing to the tree’s ecological value.
Magnolias: A Diverse Genus
Having explored the singular beauty of the Tulip Tree, we now turn our attention to another group of trees frequently admired and sometimes confused with it: the Magnolias. Unlike the Tulip Tree, a species standing virtually alone in its genus, Magnolias represent a diverse genus, Magnolia, encompassing a wide array of species, each with its own unique charm. Understanding this diversity is key to appreciating the distinctive characteristics of these beloved trees.
Unveiling the Magnolia’s Varied Forms
Magnolia trees are renowned for their large, showy flowers and lush foliage, adorning gardens and landscapes worldwide. They range from small, shrub-like specimens to towering trees, adding architectural interest and unparalleled beauty wherever they grow. However, beyond these shared qualities, lies a remarkable diversity that warrants closer examination.
The genus Magnolia showcases an impressive spectrum of traits, challenging any simplistic categorization. Some species are deciduous, shedding their leaves in autumn, while others are evergreen, maintaining their verdant foliage year-round. Flower shapes vary from elegant, upright goblets to sprawling, star-shaped blooms. This broad range of features highlights the adaptability and evolutionary success of the Magnolia lineage.
Decoding the Foliage: Size, Shape, and Texture
Magnolia leaves, while generally recognizable, exhibit considerable variation. Most Magnolia species possess leaves that range in shape from oval to elliptical, presenting a classic, refined appearance. The size of these leaves can also differ significantly, depending on the specific species and growing conditions.
Some Magnolias boast relatively small leaves, while others, such as the Magnolia macrophylla (Bigleaf Magnolia), are celebrated for their enormous foliage, reaching lengths of up to 30 inches.
The texture of Magnolia leaves can range from smooth and leathery to slightly pubescent, adding another layer of complexity to their identification. Furthermore, the distinction between deciduous and evergreen Magnolia species significantly impacts the visual landscape throughout the year. Deciduous Magnolias offer vibrant fall color before their leaves drop, while evergreen Magnolias provide year-round greenery and structure.
The Allure of Magnolia Blooms: A Kaleidoscope of Forms and Fragrances
The flowers of Magnolias are arguably their most captivating feature, contributing significantly to their ornamental value.
Their forms are incredibly diverse, showcasing everything from classic cup shapes to star-like arrangements.
The color palette of Magnolia flowers spans a spectrum of hues, from pure white and creamy ivory to shades of pink, purple, and even yellow.
Flower sizes also vary considerably, ranging from petite blooms a few inches across to enormous blossoms exceeding a foot in diameter. Many Magnolia species are also prized for their exquisite fragrance, which ranges from sweet and citrusy to spicy and exotic, further enhancing their allure.
The Bark: A Canvas of Textures and Tones
The bark of Magnolia trees offers another avenue for identification, showcasing a range of textures and colors. In general, Magnolia bark tends to be smooth when young, gradually developing more texture as the tree matures. The color can range from silvery-gray to brownish-gray, often with subtle variations that can help distinguish between different species. Some species exhibit distinctive patterns or ridges in their bark, adding to their visual interest and character. Understanding the nuances of Magnolia bark can contribute to a more accurate and complete identification of these diverse trees.
Distinguishing Features: Tulip Tree vs. Magnolia – A Side-by-Side Comparison
Having explored the individual characteristics of both the Tulip Tree and the diverse Magnolia genus, it’s time to draw a clear line between them. While subtle similarities might lead to confusion, a closer comparison reveals distinct differences that allow for accurate identification. This section offers a direct, side-by-side examination of key features.
Leaves: A Tale of Two Shapes
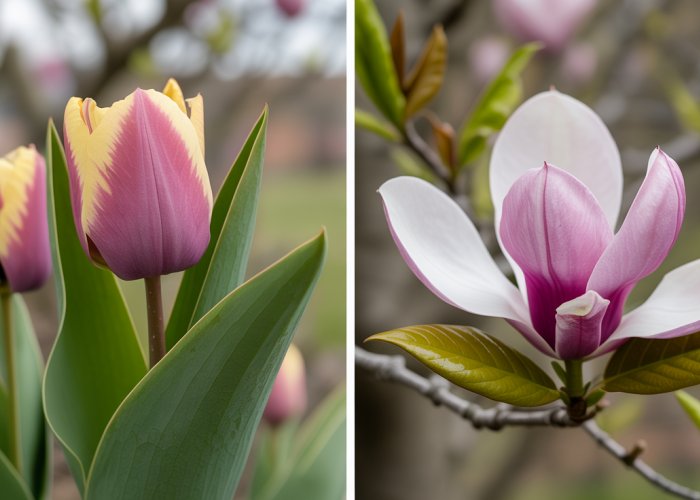
Perhaps the most readily discernible difference lies in the leaves. The Tulip Tree’s leaves are uniquely shaped, often described as tulip-shaped or lyre-shaped, with a broad, notched apex.
Magnolia leaves, on the other hand, typically exhibit an oval to elliptical form, lacking the distinctive lobes of the Tulip Tree.
The texture also differs; Tulip Tree leaves tend to be smoother, while Magnolia leaves can range from smooth to slightly leathery, depending on the species. Visual aids, such as comparative photographs or illustrations, would greatly enhance understanding of these subtle differences.
Flowers: Beyond the Bloom
The floral displays of both trees are undeniably beautiful, yet their forms are quite distinct. The Tulip Tree’s flowers, as the name suggests, bear a striking resemblance to tulips, with upright, cup-shaped blossoms in shades of greenish-yellow and orange.
Magnolia flowers, conversely, exhibit a much wider range of shapes, from elegant, upright goblets to sprawling, star-shaped blooms. Their colors span the spectrum from pure white to deep pink and even purple, depending on the specific Magnolia species.
Furthermore, while some Magnolia species boast intense fragrances, the Tulip Tree’s flowers are generally less fragrant, if at all.
Bark: A Study in Texture and Color
The bark of mature Tulip Trees is typically characterized by its deeply furrowed texture and grayish-brown color. As the tree ages, the furrows become more pronounced, creating a rugged and visually interesting pattern.
In contrast, Magnolia bark tends to be smoother, particularly in younger trees, gradually developing ridges and scales with age. The color can vary from silvery-gray to brown, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Examining bark texture and color provides another valuable clue in distinguishing between these two tree types.
Shape and Form: An Architectural Overview
The overall shape and branching patterns offer additional insights. The Tulip Tree typically exhibits a tall, straight trunk with a pyramidal or oval crown. Its branches tend to ascend, creating a symmetrical and elegant silhouette.
Magnolias, however, can display a wider range of forms, from upright and tree-like to spreading and shrub-like. Their branching patterns are often more irregular and asymmetrical, contributing to their unique character.
Size: Reaching for the Sky
Mature Tulip Trees are generally larger than most Magnolia species, often reaching heights of 70 to 90 feet or even more under optimal conditions. Some Magnolia varieties remain relatively small, shrub-like trees reaching no more than 15-20 feet.
While there are exceptions, considering the size of a mature tree can provide a useful clue in identification.
Bloom Time: A Temporal Marker
Finally, the timing of bloom can also aid in differentiation. Tulip Trees typically flower in late spring to early summer, after the leaves have fully emerged.
Magnolias, on the other hand, often bloom in early spring, before or as the leaves are emerging, although bloom times vary widely among Magnolia species. Observing when a tree flowers can be a valuable tool in distinguishing between these two frequently confused species.
Having meticulously dissected the distinguishing features of Tulip Trees and Magnolias, one might wonder why these two are so frequently mistaken. The answer lies in their shared characteristics and the subtle nuances that can blur the lines for the untrained eye.
Similarities and Sources of Confusion
While the differences between Tulip Trees and Magnolias are clear upon close inspection, several commonalities contribute to their frequent misidentification. These shared traits, combined with variations within the Magnolia genus itself, can create a landscape of potential confusion.
The Deciduous Factor
One significant overlap is the deciduous nature of many Magnolia species. Deciduous trees, by definition, shed their leaves annually, typically in the fall. The Tulip Tree is inherently deciduous.
When observing a bare tree in winter, the absence of foliage eliminates a key distinguishing factor – the unique leaf shape of the Tulip Tree. This reliance on structural features like branching patterns, which can vary considerably, makes identification more challenging.
Therefore, the shared characteristic of being deciduous can inadvertently mask crucial differences, especially during the dormant season.
The Allure of the Bloom
Both Tulip Trees and Magnolias are celebrated for their spectacular floral displays. This shared beauty can easily distract from the subtle differences in flower shape, color, and fragrance.
The sheer size and vibrancy of both Tulip Tree and Magnolia blossoms often captivate observers, leading them to overlook the finer details that differentiate the two. The visual impact is undeniable, and the initial impression can often lead to a premature conclusion.
The "Magnolia-like" Appearance
Furthermore, certain Magnolia species exhibit flower shapes that, at a glance, might resemble the more upright form of Tulip Tree blossoms. While a closer look reveals distinctions, the initial impression can be misleading.
Adding to the potential for misidentification is the variation within the Magnolia genus itself. With numerous species and cultivars, the range of flower forms is considerable, and some may bear a superficial resemblance to the Tulip Tree’s cup-shaped blooms.
This underscores the importance of considering multiple characteristics, rather than relying solely on flower shape, for accurate identification.
Tulip Tree vs. Magnolia: FAQs
Still unsure how to tell the difference between a tulip tree and a magnolia? Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify the key distinctions.
What is the biggest difference between a tulip tree and a magnolia?
The most noticeable difference is the leaf shape. Tulip tree leaves are uniquely shaped with four distinct lobes, almost like a tulip silhouette. Magnolia leaves are typically oval or elliptical and have smoother, more rounded edges. Also, flowers are noticeably different with tulip trees having cup-like greenish-yellow flowers with orange bands, and magnolias having larger, showier blooms.
Are tulip trees magnolia?
No, tulip trees are not magnolias. While both are flowering trees and belong to the plant kingdom, they belong to different families. Tulip trees are in the Liriodendron genus, while magnolias belong to the Magnolia genus. They are related but distinct.
How can I tell the difference when the trees aren’t flowering?
Focus on the leaves and bark. Tulip tree bark is generally smoother and gray-brown with diamond-shaped patterns as the tree matures. Magnolia bark is often rougher and more textured. Also examine leaf shape as described above.
Do tulip trees and magnolias grow in the same locations?
Yes, they can often grow in similar regions, particularly in the eastern United States. Both thrive in well-drained soil and prefer full sun to partial shade. However, specific magnolia varieties might have different climate preferences, so check local growing conditions before planting.
So, next time you’re strolling through the park and wondering, are tulip trees magnolia, remember those key differences we talked about! Happy tree-spotting!